Black Period Blood
Share
When observing the nuances of menstrual health, the color of period blood can offer significant insights. Black period blood, often a startling sight, is typically the result of blood that has aged and oxidized within the uterus, commonly appearing towards the end of the menstrual cycle. Understanding the spectrum of period blood colors, from bright red to dark black, is crucial for recognizing what is normal and what may require medical attention. This article delves into the reasons behind the color variations, their potential health implications, and when it is advisable to seek professional guidance.
Key Takeaways
-
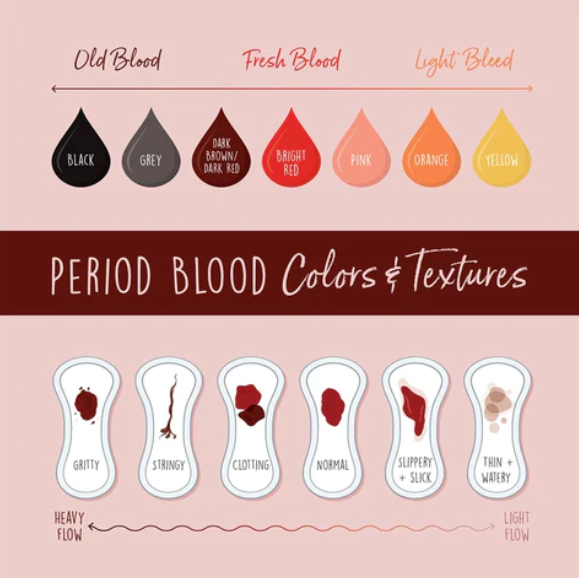
Black period blood is usually 'old blood' that has been oxidized, indicating it has been present in the uterus for some time and often appears at the end of a period.
-
Period blood can range from bright red at the beginning of menstruation, indicating fresh blood, to darker tones such as brown or black as it ages and undergoes oxidation.
-
While variations in period blood color are typically normal, consistently dark blood, such as brown or black, may warrant a consultation with a healthcare provider.
-
The color of period blood is influenced by factors such as the rate of flow, the duration of menstruation, and hormonal changes within the body.
-
Understanding the differences between hymen blood, which is usually bright red and fresh, and period blood, which can vary widely in color, is important for menstrual health awareness.

Understanding the Spectrum of Period Blood Colors
The Significance of Color Variation in Menstrual Blood
The colors of menstrual blood are not merely a matter of aesthetics; they are indicative of various physiological processes and can signal changes in a woman's health. The significance of color variation in menstrual blood is profound, as it can provide insights into the timing of discharge, the oxidation state of the blood, and potential health issues. For instance, the transition from bright red to darker tones can be a natural part of the menstrual cycle, reflecting the length of time the blood has been exposed to air and the degree of oxidation that has occurred.
Menstrual blood color can range from bright red to black, with each shade potentially conveying a different message about one's health. To better understand these variations, consider the following points:
-
Bright red blood often indicates fresh blood that has not had time to oxidize.
-
Darker blood, including brown or black, suggests older blood that has had more time to oxidize.
-
The presence of other symptoms, such as severe cramping or spotting between periods, can also influence the interpretation of blood color.
It is essential to monitor these changes and understand what they may imply about your menstrual health. Recognizing the normal spectrum of colors can help distinguish between typical fluctuations and those that may warrant further investigation.
Comparing Hymen Blood and Period Blood
Understanding the differences between hymen blood and period blood is crucial for recognizing normal bodily functions and identifying any potential health concerns. Hymen blood is typically a one-time occurrence, resulting from the tearing or stretching of the hymen, which may happen due to various activities such as sexual intercourse, physical exertion, or even the insertion of tampons. In contrast, period blood is a regular monthly event that signifies the shedding of the uterine lining when pregnancy does not occur.
The characteristics of hymen blood compared to period blood can be summarized as follows:
-
Cause: Hymen blood is caused by physical changes to the hymen, while period blood is a hormonal process.
-
Frequency: Hymen blood occurs sporadically, often just once, whereas period blood is a cyclical occurrence.
-
Color: Hymen blood is usually bright red, indicating freshness, while period blood can vary from bright red to brown or black due to oxidation.
-
Amount: Hymen blood is minimal, often just spotting, while period blood can range from light to heavy flow.
-
Duration: Hymen blood lasts a short time, typically a day or two, while period blood lasts between 3 to 7 days.
While hymen blood is usually minimal and can occur sporadically, period blood is a regular and cyclical occurrence in a woman's reproductive life.
The Role of Hemoglobin in Blood Coloration
Hemoglobin, the iron-containing protein in red blood cells, is pivotal in determining the color of menstrual blood. Its primary role is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body, but it also imparts the red hue to blood. When menstrual blood is exposed to air, hemoglobin undergoes oxidation, which can lead to a change in color from red to darker shades, such as brown or black.
The oxidation process is a natural occurrence and varies from person to person. Factors such as the length of time the blood remains in the uterus before being expelled and the rate of flow can influence the extent of oxidation. For instance, a slower flow or blood that has pooled in the uterus for a longer time is more likely to appear darker when it is finally shed.
Understanding the nuances of hemoglobin's role in blood coloration is essential for interpreting the various shades of menstrual blood. It is a complex interplay of biological processes that can signal different things about one's health.
Decoding the Shades: From Bright Red to Black
Bright Red Period Blood and Its Implications
Bright red period blood is often observed at the onset of menstruation, signifying that the blood is fresh and the flow is beginning. This vibrant coloration is a hallmark of a healthy menstrual cycle and indicates that the blood has not had time to oxidize. The presence of bright red blood can be reassuring, as it typically means the menstrual flow is proceeding normally.
However, it's important to note that while bright red blood is generally considered normal, it can also be a symptom of other conditions. For instance, bright red blood may signal the presence of uterine polyps or fibroids, which are benign growths that can cause a heavier flow. Additionally, conditions such as adenomyosis, characterized by the thickening of uterine tissue, may lead to painful periods accompanied by bright red blood.
The color of menstrual blood can provide valuable insights into one's reproductive health. Monitoring these changes is crucial, as they can be indicative of various health conditions.
For further understanding of menstrual health and related topics, readers are encouraged to explore our other blogs, which delve into the nuances of menstrual cycle variations and the implications of different period blood colors.
The Transition to Darker Tones: Brown and Black Period Blood
As the menstrual cycle progresses, the color of period blood can transition from a bright red to darker shades, indicating various stages of the cycle. Brown period blood often marks the end of menstruation, appearing just before the bleeding ceases. This darkening is a natural consequence of the blood's prolonged exposure to air, leading to oxidation.
-
Bright red blood signifies fresher blood, typically seen at the start of a period.
-
Dark red blood may appear after periods of inactivity, such as overnight.
-
Brown to black blood indicates older, oxidized blood, often at the end of the cycle.
The appearance of black period blood is not inherently alarming. It is simply blood that has been present in the uterus for an extended period, allowing for full oxidation. This is most common towards the end of the menstrual flow when the rate of discharge slows down.
While the presence of brown or black blood is usually part of a normal menstrual cycle, it is essential to monitor any abrupt changes in color.
Factors Influencing the Darkening of Menstrual Blood
The darkening of menstrual blood is a phenomenon influenced by several factors. The primary factor is the duration the blood remains in the uterus and vagina, leading to oxidation. This process, as explained by experts, causes the blood to darken over time. For instance, blood that appears darker in the morning or after prolonged periods of lying down suggests it has had more time to oxidize.
Other factors contributing to the darkening of menstrual blood include the presence of blood clots and the flow's heaviness. Blood clots, which are often dark red in color, can indicate a heavier menstrual flow. It is important to note that menstrual blood can vary from bright red to brown or black as it ages and undergoes oxidation.
The spectrum of period blood colors is a reflection of various physiological processes, and understanding these can provide insights into one's menstrual health.
Additionally, external factors can also play a role. For example, recent findings have raised concerns about the impact of environmental contaminants, such as PFAS detected in Thinx menstrual care items, on menstrual health. It is crucial to stay informed about such developments by following updates on our blog.
-
Oxidation due to prolonged presence in the uterus
-
Blood clots indicating a heavier flow
-
Environmental contaminants affecting menstrual health
The Health Implications of Black Period Blood
When to Consider Black Period Blood as Normal
In the diverse spectrum of menstrual blood colors, black period blood often signifies the end of the menstrual cycle. This coloration is typically not a cause for concern, as it represents blood that has had time to oxidize within the uterus, indicating it is 'old blood'. This phenomenon is most common when the menstrual flow has decreased, marking the conclusion of the period.
It is crucial to recognize that variations in period blood color are a normal part of the menstrual experience. The transition from bright red to darker shades, including black, can occur naturally. However, understanding what is typical for one's body is essential, as individual experiences with menstruation can vary greatly.
While the appearance of black period blood can be disconcerting, it is often a normal part of the menstrual process, particularly towards the end of the cycle.
If the occurrence of black period blood is accompanied by other symptoms or is a new development, it may warrant further investigation. In such cases, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable to rule out any potential health concerns.
Potential Health Concerns Associated with Dark Menstrual Blood
While the presence of dark menstrual blood, including shades of brown and black, can be a normal part of the menstrual cycle, particularly at the beginning or end, it may also signal underlying health issues. Consistently observing black period blood should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider, as it could indicate hormonal imbalances, such as a deficiency in progesterone, or other medical conditions.
It's essential to consider the context of your menstrual cycle and overall health when evaluating the color of menstrual blood. Factors such as age, diet, and hereditary conditions can influence menstrual blood color and consistency.
For instance, the presence of PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) detected in Knix products has raised concerns about the potential impact of environmental toxins on menstrual health. If you're experiencing additional symptoms like severe cramping or spotting between periods, it's crucial to address these with your doctor.
Here are some signs to watch for that may accompany black period blood and warrant medical attention:
-
Severe abdominal cramps
-
Spotting between periods
-
Larger than normal blood clots
-
Unusual symptoms not typically experienced during your cycle
The Importance of Monitoring Menstrual Blood Color Changes
Monitoring the color of menstrual blood is crucial for understanding one's overall health. Sudden or unfamiliar changes in the color of menstrual blood may indicate underlying health issues and warrant further investigation. It is essential for individuals to recognize what is normal for their bodies and to be vigilant about any deviations from their typical menstrual patterns.
-
Bright Red: Often indicates fresh blood and a steady flow.
-
Dark Red/Brown: May occur at the beginning or end of a period, representing older blood.
-
Black: Can be a sign of oxidized blood, but if accompanied by other symptoms, it could suggest a health concern.
While variations in menstrual blood color are common, persistent changes should not be overlooked. Black period blood, in particular, can be normal when it appears without other symptoms, but if it persists or is accompanied by pain or unusual odors, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
Physiological Explanations for Color Changes in Menstrual Blood
The Oxidation Process and Its Effects on Blood Color
The spectrum of period blood colors can be attributed to various factors, with the oxidation process playing a pivotal role. Oxidation refers to the chemical reaction that occurs when blood is exposed to air, leading to a change in color. As blood remains in the uterus and vagina, it undergoes this process, transitioning from a bright red to darker shades, including brown and ultimately black.
The duration of blood within the reproductive system is a key determinant of its color. The longer the blood is retained before being discharged, the more pronounced the oxidation, and consequently, the darker the color. This is particularly evident in the case of black period blood, which signifies that the blood has been present for an extended period.
The color change in menstrual blood due to oxidation is a natural and expected phenomenon, indicating the age of the blood rather than a health issue.
Hormonal Influences on Menstrual Blood Color
Hormonal fluctuations play a pivotal role in determining the color of menstrual blood. Estrogen and progesterone, the primary female hormones, regulate the menstrual cycle and influence the shedding of the uterine lining. Variations in hormone levels can lead to changes in blood color, ranging from bright red to darker shades like brown or black. For instance, low estrogen levels may result in lighter bleeding and a brighter hue, while higher levels can cause a heavier flow and darker blood.
The menstrual cycle's phases also impact blood color. During ovulation, some women may notice a brighter red shade, indicative of fresh blood. Conversely, the luteal phase, which occurs post-ovulation, can be associated with darker blood due to the blood's longer exposure to oxygen before being expelled.
-
Estrogen levels
-
Progesterone levels
-
Phase of menstrual cycle
Hormonal changes are not only influential in the color of menstrual blood but also in the overall menstrual experience. These changes can be subtle or more pronounced, and understanding them can provide valuable insights into one's reproductive health.
Understanding the Duration and Flow Impact on Blood Shade
The duration and flow of a menstrual cycle can significantly influence the color of period blood. A longer menstrual cycle often results in darker shades of blood, as the blood has more time to oxidize within the uterus. This is particularly evident when comparing the lighter, fresher hue of blood at the beginning of a period to the darker tones that may appear as the cycle progresses.
The flow rate also plays a crucial role. A heavier flow tends to flush out blood more quickly, resulting in a brighter red color. Conversely, a lighter flow may lead to a slower discharge, giving the blood ample time to darken as it oxidizes. It's important to note that variations in color are normal and can fluctuate from cycle to cycle.
While the color of period blood can be a helpful indicator of overall reproductive health, it is not the sole factor to consider. Consistent monitoring and understanding of one's menstrual cycle are essential for recognizing any significant changes that may warrant further investigation.
Navigating Concerns and When to Seek Medical Advice
Differentiating Between Normal and Abnormal Menstrual Colors
Understanding the nuances of menstrual blood colors is crucial for recognizing when a change may be indicative of an underlying health issue. Normal variations in color can range from bright red to dark brown, often reflecting the age of the blood and the speed of the flow. However, certain colors, particularly gray and off-white, should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider.
It's essential to be vigilant about any sudden or unfamiliar changes in period blood color, as these could signal potential health concerns.
To help differentiate between normal and abnormal menstrual colors, consider the following points:
-
Bright red blood is typically fresh and seen at the start of a period.
-
Darker tones, including brown and black, may appear as the blood oxidizes over time.
-
Unusual colors like gray or off-white, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, warrant medical attention.
Guidelines for Consulting Healthcare Professionals
When experiencing unusual menstrual colors, particularly black period blood, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Seeking medical advice is essential when changes persist or are accompanied by other symptoms. It is not advisable to self-diagnose or rely solely on information found online, as each individual's health situation is unique.
-
Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider if you notice significant changes in menstrual blood color.
-
Prepare a list of symptoms and any relevant medical history to discuss during your consultation.
-
Consider tracking your menstrual cycle and symptoms using a journal or app to provide detailed information to your physician.
While occasional variations in menstrual blood color can be normal, persistent or dramatic changes warrant professional evaluation.
Interpreting Menstrual Color Changes in the Context of Overall Health
Understanding the nuances of menstrual blood color is crucial in assessing one's overall health. The color, texture, and flow of period blood can be indicative of various health conditions, and it is essential to recognize what is normal for your body. Regular monitoring of these changes is a proactive step towards maintaining reproductive health.
-
Bright Red: Normal, fresh blood
-
Dark Red/Brown: Blood that has taken longer to exit the uterus
-
Black: Oxidized blood, possibly older blood at the end of the cycle
It is important to note that while some variations in color are normal, persistent changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
In the context of overall health, menstrual blood color should not be viewed in isolation. It is one piece of a larger health puzzle that includes other vital signs and symptoms. If you are experiencing other unusual symptoms, such as severe cramping or spotting between periods, it is advisable to consult with a gynecologist.
Understanding the Spectrum of Period Blood Colors
In conclusion, the range of colors in period blood, from bright red to dark black, is a natural phenomenon largely influenced by the oxidation process and the duration it remains in the uterus. While the sight of black or brown period blood can be disconcerting, it is typically a sign of the body's normal functioning, marking the end of the menstrual cycle. However, persistent changes in color, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying conditions. It's important to remember that each individual's experience with menstruation is unique, and being informed about the variations in period blood can help demystify the process and promote a proactive approach to reproductive health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does black period blood indicate?
Black period blood is typically an indication of 'old blood' that has been oxidized. This usually occurs at the end of your period when the flow has slowed down significantly.
Is it normal to have brown period blood at the beginning of my period?
While brown period blood is more common at the end of your period, it can also appear at the beginning. This is often due to older blood that has taken longer to exit the vagina. However, consistently brown or black period blood may require investigation by a doctor.
How does the color of period blood change throughout the menstrual cycle?
Period blood can range from bright red at the start of your period, indicating fresh blood, to darker shades like brown or black as the blood ages and oxidizes. The color change is often due to the time it takes for blood to pass through the uterus.
Can the color of my period blood be an indication of a health issue?
While variations in period blood color are typically normal, certain colors can indicate health issues. For instance, consistently dark period blood could be a sign of hormonal imbalances or other conditions and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
What is the difference between hymen blood and period blood?
Hymen blood is usually bright red and fresh, typically lasting a day or two. Period blood can vary from bright red to brown or black depending on its age and oxidation, with a menstrual cycle typically lasting 3-7 days.
When should I seek medical advice regarding the color of my period blood?
You should consult a healthcare professional if you notice significant changes in the color of your period blood, especially if it's consistently brown or black, or if you experience other symptoms such as pain or unusual discharge.
